Seven Wonders is a CFD broker specializing in global forex trading services
Seven Wonders is a CFD broker specializing in global forex trading services
Forex trading, also known as foreign currency investment, refers to the conversion of one currency into another by individuals, businesses, or central banks. Although many forex transactions are for practical purposes, a larger portion of currency conversion is aimed at profit. With daily currency conversion amounts exceeding \$5 trillion, the forex trading market has become the largest financial market globally, leading to significant fluctuations in certain currency prices. The volatility of the forex market attracts some traders; however, the potential for higher profits comes with greater risks.
An exchange rate refers to the ratio at which one currency can be exchanged for another, typically presented in the form of a currency pair, such as GBP/USD. Exchange rates can be floating (changing daily) or fixed, such as the exchange rate for the Qatari Rial to the US Dollar fixed at \$1/3.64 QR.

People have various reasons or needs to participate in the forex market. However, the following two are the most common motivations for forex trading:
Purchasing Goods or Services Abroad
This is the form of forex trading that most people are familiar with. When individuals or companies need to purchase goods or services in different currencies, they must trade forex. Therefore, trading forex is an essential part of industries like international trade. Although practical forex trading occurs continuously, it actually only accounts for a small fraction of all currency transactions.
Speculation
Most forex trading is actually aimed at making a profit. Traders focus on the fluctuations in forex prices and do not actually deliver the currencies themselves; their goal is to profit from the changes in the forex market. Large investors can engage in numerous forex transactions in a single day, continuously responding to and predicting currency price changes. Currency trading is relatively convenient and is a highly liquid asset, which is one reason forex volatility is higher than in other markets.
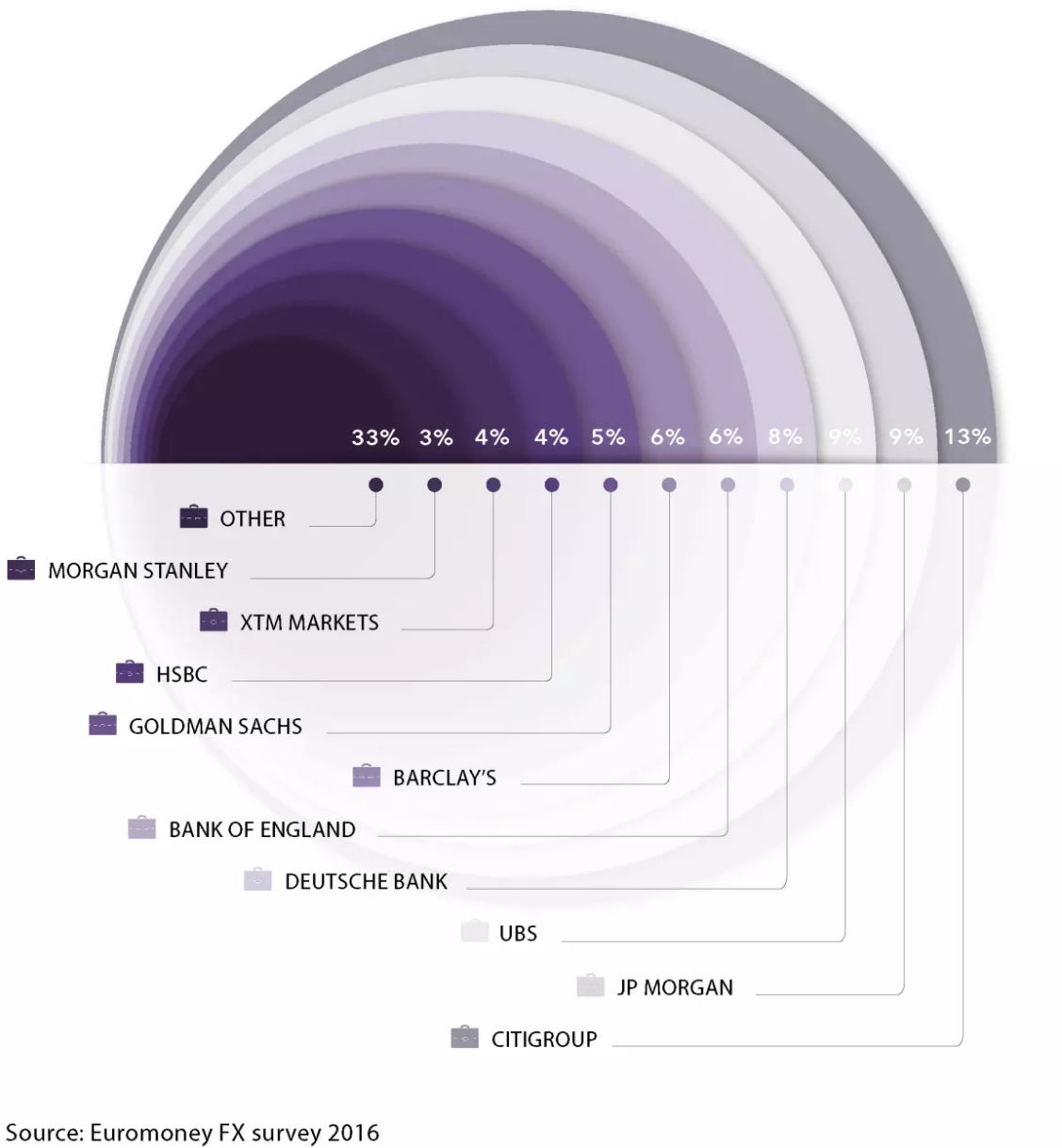
Major international banks such as Citigroup, UBS, and Barclays are the main players in forex trading, aiming to profit from price fluctuations in the market. The top four banks account for about 50% of all forex trading. However, individual forex trading is also prevalent in the market. Governments and central banks also participate in forex trading to control the money supply of their economies. Consumers, companies, and financial institutions are involved in currency exchange during cross-border trade, overseas travel, and foreign market investments.
Like most financial markets, forex price changes are primarily driven by supply and demand. Banks and other investors seek to invest capital in stronger economies. Therefore, if positive news about a specific region emerges, it usually stimulates investment, leading to increased demand for that region's currency. Unless the supply of that currency also increases accordingly, the gap between supply and demand will cause its price to rise. Similarly, negative news can lead to decreased investment, causing currency prices to fall. Thus, currencies typically reflect the economic health of the region they represent.
Many factors can influence the supply of a specific currency, including short-term, medium-term, and long-term factors.
Short-term factors: Risk appetite, volatility, changes in commodity prices, interest rate changes, and positioning.
Medium-term factors: Current account surplus/deficit, fiscal policy, political risk, bond yield spreads, and other economic growth indicators.
Long-term factors: Purchasing power parity, net foreign assets, and terms of trade.
Market sentiment also plays an important role in driving currency prices. If traders believe that a currency is developing in a certain direction and trade based on that belief, they may persuade others to follow suit, thereby increasing or decreasing demand. However, demand is not the only variable affecting currency prices. The supply of currency is controlled by central banks, which can announce policies that significantly influence their currency prices. For example, quantitative easing refers to injecting more currency into the economy, which naturally causes the currency price to fall.
Unlike stocks and other financial products, forex trading does not take place on an exchange. Currencies are traded directly between buyers and sellers in the over-the-counter (OTC) market. In other words, the forex market trading center operates between a global network of banks, distributed across major OTC markets in different time zones such as London, New York, Sydney, and Tokyo. Since forex trading does not require a central location, it can be conducted 24 hours a day.
To engage in forex trading, you need a forex broker. Alternatively, you can participate in forex trading through derivatives such as contracts for difference (CFDs).